Artificial Intelligence (AI) has moved far beyond hype—it is now a critical driver of business performance, efficiency, and competitive advantage. Yet, for many executives, the challenge isn’t whether to use AI but how to integrate AI into existing systems without disrupting operations.
This AI integration guide is written specifically for business leaders who want to understand the opportunities, challenges, and best practices of adopting AI across an enterprise. Whether you lead a multinational corporation or a growing mid-sized firm, this guide provides a practical roadmap for implementing AI in a way that is scalable, secure, and strategically aligned with your goals.
Why AI Integration Matters for Business Leaders
AI is no longer optional—it’s becoming a baseline expectation in most industries. From personalized marketing and predictive analytics to automated supply chains and enterprise decision-making, organizations that successfully adopt AI outperform those that don’t.
According to McKinsey, companies that fully integrate AI into their business processes report 20–30% improvements in efficiency and significantly higher revenue growth. On the other hand, businesses that only experiment with AI in isolated use cases often fail to capture long-term benefits.
The difference lies in integration—making AI part of the organization’s core operations, not just an add-on tool.
The Challenges of Integrating AI into Existing Systems
For executives considering enterprise AI adoption, the road is not without obstacles. Common challenges include:
Legacy Infrastructure
Many enterprises rely on outdated systems that don’t easily support modern AI tools. Integration often requires middleware or cloud migration strategies.
Data Silos
AI thrives on data, but in most organizations, data is fragmented across departments and formats. Breaking down silos is essential.
Change Management
Employees may resist automation due to fear of job loss or workflow disruption. Strong leadership and training are critical.
Cost and ROI Uncertainty
Building and scaling AI can be expensive, and leaders often struggle to measure ROI in the early phases.
Regulation and Compliance
Especially in industries like healthcare, finance, and logistics, integrating AI into existing systems must adhere to strict compliance frameworks.
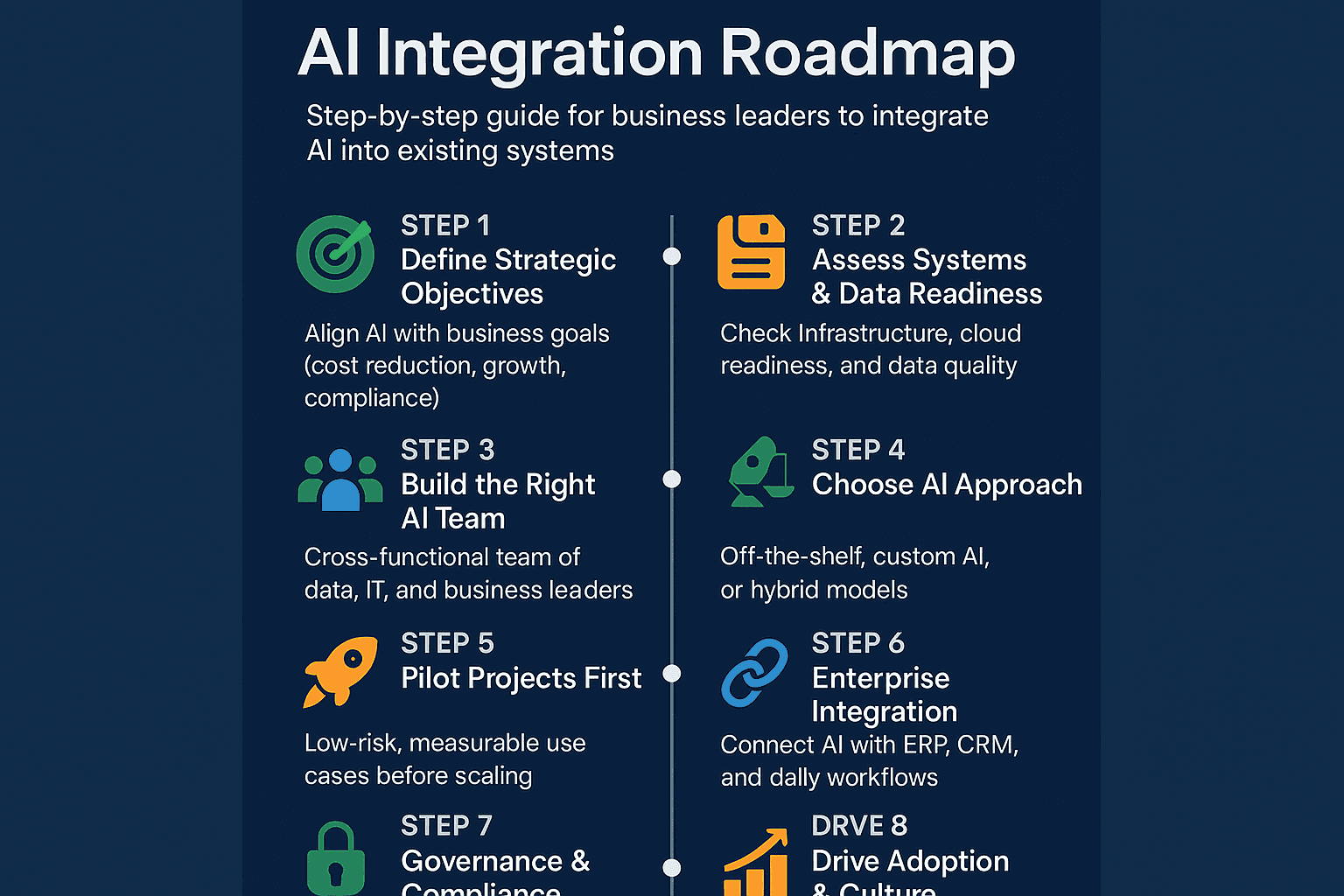
Step 1: Define Strategic Objectives
The first step in this AI integration guide is not about technology—it’s about strategy. Business leaders should ask:
What business outcomes do we want from AI?
Are we focusing on cost reduction, revenue growth, risk mitigation, or innovation?
How does AI support our broader corporate strategy?
For example, a bank may prioritize fraud detection and compliance, while a retailer may focus on personalized customer experiences. Defining objectives ensures that AI projects are not isolated experiments but tied directly to measurable business outcomes.
Step 2: Assess Current Systems and Data Readiness
Before integrating AI into existing systems, leaders must assess:
System Compatibility: Are ERP, CRM, or supply chain systems ready to interface with AI tools?
Cloud vs. On-Premise: Do we need to modernize infrastructure before deploying AI?
Data Quality: Is the data clean, accessible, and sufficient to train AI models?
A data maturity assessment can reveal whether your organization is ready for enterprise AI adoption or if foundational work is needed first.
Step 3: Build the Right AI Integration Team
Successful AI projects require collaboration between technical experts and business stakeholders. A typical AI integration team includes:
Chief Data/AI Officer (CDAO) – provides strategic direction.
Data Engineers & Scientists – design and train models.
IT & System Architects – ensure seamless integration into existing systems.
Business Process Owners – align AI with workflows.
Change Management Leaders – drive adoption among employees.
Business leaders don’t need to be AI experts—but they do need to champion integration efforts and ensure cross-departmental alignment.
Step 4: Choose the Right AI Approach
When it comes to enterprise AI, leaders must choose between:
Off-the-Shelf AI Tools – Faster, cheaper, and easier to deploy but less customizable.
Custom AI Solutions – Tailored models designed around specific business needs and proprietary data.
Hybrid Approach – Start with pre-built tools, then evolve into custom models as needs grow.
The right choice depends on budget, scalability goals, and the strategic importance of AI in your sector.
Step 5: Pilot Projects Before Full Integration
One of the most effective methods of integrating AI into existing systems is starting small. Business leaders should:
Select a low-risk, high-visibility use case.
Define clear success metrics.
Run the pilot alongside existing systems to compare performance.
Scale gradually once results are validated.
For example, a logistics firm might start with an AI model predicting delivery delays before scaling up to route optimization across the entire fleet.
Step 6: Integration into Enterprise Systems
Once a pilot succeeds, it’s time to scale AI across the organization. This involves:
API & Middleware Integration: Connecting AI models to ERP, CRM, and other enterprise platforms.
Automation Workflows: Embedding AI into daily business processes rather than using it as a separate tool.
Monitoring & Feedback Loops: Continuously measuring AI’s impact and retraining models when needed.
Here, enterprise AI is no longer just a “project”—it becomes part of the operational backbone.
Step 7: Governance, Security, and Compliance
No AI integration guide is complete without addressing governance. Business leaders must:
Establish clear AI ethics policies (transparency, fairness, accountability).
Implement security protocols for sensitive data.
Ensure compliance with industry regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or SOX.
Create audit trails to monitor AI decision-making.
Failing to address governance can create reputational and legal risks that outweigh AI’s benefits.
Step 8: Drive Adoption and Cultural Change
AI integration is not just a technical upgrade—it’s a cultural shift. Business leaders must:
Communicate AI’s role as an enabler, not a replacement for human talent.
Invest in training programs that upskill employees to work alongside AI.
Incentivize adoption by linking AI-driven outcomes to business performance goals.
Organizations that treat AI as a partnership between humans and machines see higher adoption and long-term success.
Real-World Examples of Enterprise AI Integration
Retail: Walmart integrates AI into inventory management, reducing stockouts and improving supply chain forecasting.
Finance: JPMorgan Chase uses AI to automate legal document review, saving thousands of hours annually.
Healthcare: Mayo Clinic integrates AI into diagnostic systems to improve detection accuracy and patient outcomes.
Manufacturing: Siemens deploys predictive maintenance AI across factories, cutting downtime costs.
These examples show that integrating AI into existing systems is not theoretical—it’s already delivering results in multiple industries.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Even with strong leadership, AI integration can fail if leaders:
Pursue AI without clear business goals.
Underestimate data readiness challenges.
Over-rely on technology vendors without building internal capability.
Neglect change management and workforce engagement.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires proactive leadership and a balanced strategy of technology and human adoption.
Measuring Success: KPIs for AI Integration
To ensure enterprise AI projects deliver value, leaders should measure:
Operational Efficiency Gains – Reduction in costs, time, or errors.
Revenue Impact – Increases in sales, retention, or customer lifetime value.
Risk Reduction – Fewer compliance breaches, fraud incidents, or operational risks.
Employee Productivity – Higher output per worker or improved decision-making support.
Customer Experience – Improved satisfaction scores or reduced churn.
Tracking these metrics helps validate ROI and secure future investment in AI.
The Future of Enterprise AI
Looking ahead, AI integration will move from being an advantage to a necessity. Trends shaping the future include:
Generative AI for product design, marketing, and customer interaction.
AI-First Enterprises where automation is the default, not the exception.
Hyper-Personalization in retail, banking, and healthcare.
Regulatory Frameworks that standardize responsible AI use.
AI + IoT Convergence in manufacturing and logistics.
Business leaders who start integrating AI today will be better prepared for these shifts.
Conclusion
This AI integration guide makes one thing clear: integrating AI into existing systems is not a one-off project but an enterprise-wide transformation.
Start with strategy and data readiness.
Build the right teams and governance frameworks.
Pilot before scaling.
Drive adoption with cultural change.
For business leaders, AI is not just about technology—it’s about building the foundation for long-term resilience, competitiveness, and growth.
The companies that succeed will be those that see AI not as an external tool but as a core enterprise capability—woven into every decision, every workflow, and every customer interaction.